Beyond the simple amount to be paid on the electricity bill, better known as “the light bill,” this document contains valuable information about: average energy consumption in an establishment, the type of rates applied, and other charges that directly impact operating costs.
Therefore, knowing how to read the data provided by the Federal Electricity Commission (CFE) on your electricity bill is essential for efficiently managing energy demand in any company or industrial sector.
In addition, it is important to consider that receipts for a residence or small business are not read in the same way as those for a large company. The main difference is that commercial receipts (GDMTH, DIST, DIT rates) are charged based on an hourly rate.
Features of the CFE electricity bill
The CFE bill consists of several key sections that provide detailed information on consumption and associated costs. Its most important features are:
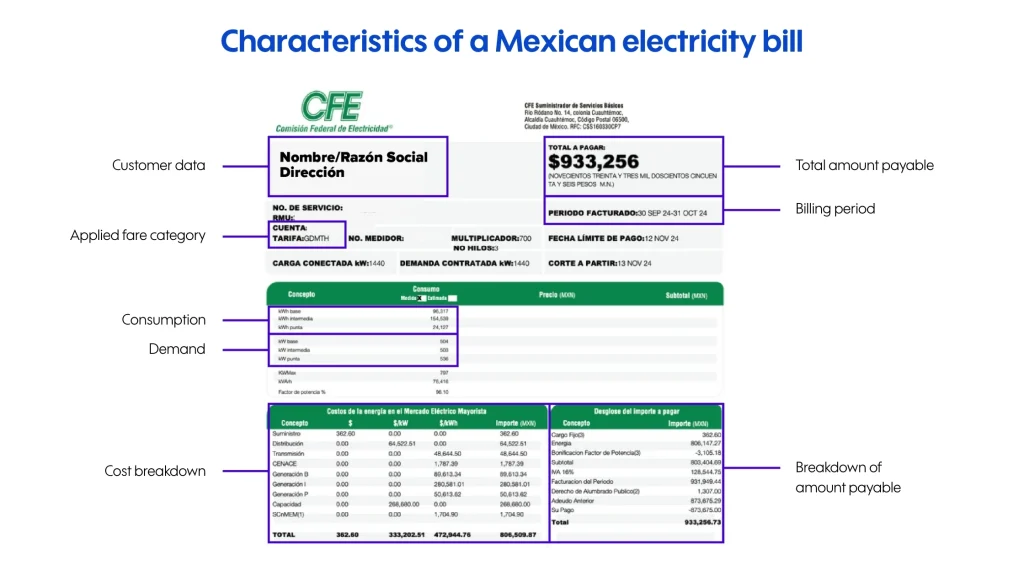
- Customer details: user’s name or business name, supply address, and service number.
- Billing period: time interval to which consumption corresponds. It also shows the billing period and the payment due date. This is crucial for financial planning and preventing power cuts due to non-payment.
- Applied tariff category: this indicates the type of user and the required demand or, in other words, the amount of energy used in the property. There are tariffs for large companies such as GDMTH, DIST, and DIT.
- Total amount payable: includes the cost of the energy consumed and other items such as VAT, charges for or against the power factor, and any previous debts.
- Meter readings: consumption records at the beginning and end of the period. This segmentation is vital to understanding how consumption is distributed and how rates are applied.
- Consumption in kWh: the amount of energy consumed during the billing period. Consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh) refers to the distribution of consumption in the base, intermediate, or peak categories and is charged in pesos per kilowatt hour consumed ($/kWh). The cost will depend on two factors: whether that consumption was during the base, intermediate, or peak period and also varies according to the fixed charge made by the CFE for its operating costs.
- Demand in kW: This is the maximum demand recorded by CFE in each period, the highest peak of the month. However, the charge in pesos per kilowatt ($/kW) only considers the highest peak or maximum demand recorded during the peak period. This is charged on the bill as “Capacity.”
- Historical consumption graph: Some bills provide a visualization of consumption in previous periods, which helps identify trends and evaluate the impact of energy efficiency measures.
How to read your electricity bill correctly?
The most important items to look for when reading an electricity bill are the billing period, key payment dates, and service suspension dates. You should also check the consumption details, which are shown in kWh, the peak demand, which is shown in kW, and the itemized costs related to energy demand and consumption during the billing period.
Additionally, in Mexico, there are different rates on CFE electricity bills for industrial companies, which are determined based on the amount of energy they have contracted, taking into account their average consumption. For example, to know how to interpret your electricity bill, it is important to know whether the rate is Gran Demanda en Media Tensión ordinaria (GDMTO) or Gran Demanda en Media Tensión horaria (GDMTH).
The correct reading of the bill with the GDMTO rate is for companies with contracted demands of less than 100 kW per month and with a fixed energy cost 24 hours a day. This category is billed every two months.
In contrast, with the GDMTH tariff, designed for companies with demands greater than 100 kW, the billing period is monthly and is governed by different schedules: Base, Intermediate, and Peak, where each kWh has a different cost depending on the time of use. In addition, a capacity charge is included, calculated based on the maximum peak demand for the month.
How to calculate a company’s electricity consumption in kWh?
Remember that energy consumption is measured in kWh. Below, we will see how two of the different CFE rates for businesses and industries are calculated: GDMTO and GDMTH.
- On electricity bills with the GDMTO tariff, there is an item called Multiplier. This number is assigned by CFE to multiply the difference between meter readings and obtain how many kilowatt-hours (kWh) the company consumes. There is also a number in the “Difference” column, which is the result of subtracting the previous reading from the current reading. Taking into account the above, to find out the kWh consumption on the electricity bill, multiply the Multiplier number by the Difference number and the total will be the consumption in kWh. It is important to monitor this consumption regularly to detect significant variations that may indicate inefficiencies or problems in the electrical system.
- On electricity bills with the GDMTH tariff, the energy consumed is shown directly in kWh and the demand in kW on the bill. The charge for this tariff is shown in the second box on the bill, where the energy consumed in the three tariff periods appears: Base, Intermediate, and Peak.
Now, to calculate the cost of the Distribution and Transmission items, multiply the cost of each item by the energy or demand consumed (distribution kW and transmission kWh).
Finally, to calculate the Capacity, we obtain this data using a specific formula published on the CFE website, which is essential for understanding the costs on the bill.
The price of “Capacity” is calculated by taking the lower value between the maximum demand recorded during “Peak” hours and the result of the formula used by CFE, which considers monthly consumption, hours, and days of the month. This ensures a more accurate cost based on the company’s consumption behavior.
It is important to understand that the most expensive item on the entire bill is Capacity.
Tools to optimize your CFE bill
The implementation of advanced technologies can significantly contribute to optimizing energy consumption and lowering CFE bill prices. Some tools that companies can use in industrial environments are:
Energy monitor
The electrical energy monitor is essential for advanced energy management as it not only measures total energy consumption in kWh, but also breaks down energy use by specific devices, allowing for detailed analysis.
This tool uses WiFi or Ethernet to transmit data in real time and allows energy consumption to be monitored from mobile devices or computers, making it easy to identify consumption patterns and areas of inefficiency. This enables decisions to be made to improve the electricity demand in a specific area.
Using an energy monitor provides companies with information about their consumption, which can help them make decisions to make their consumption more efficient. It also allows them to analyze electrical parameters and comply with the Grid Code (to avoid penalties for non-compliance). Information is power.
You may be interested in: What tools are available for measuring electrical energy?
Solar panels
Over the last five years, solar panels have become an essential technology for harnessing solar energy. In addition to generating clean energy, they are a sustainable, flexible, and efficient solution for meeting energy demands.
Because solar panels allow energy to be generated on site, reducing losses associated with electricity transmission and distribution, the CFE reduces the value of the electricity bill for users who have these installations. The exact amount depends on several factors, such as the user’s location and consumption habits.
On the other hand, generating energy during daylight hours will allow the demand on CFE during intermediate hours to decrease, thereby reducing the total cost of the bill. At the same time, this allows the company that installs solar panels to be more sustainable by generating clean energy.
BESS: battery energy storage system
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) play a key role in reducing energy costs. Using lithium-ion batteries, BESS store energy during off-peak hours (base load) and release it during peak hours (peak load), thus reducing the amount of energy consumed during this period (kWh) and cutting demand peaks (kW).
The use of BESS systems operated by Industronic software directly reduces electricity bills by up to 35%.
There is also a significant sustainable benefit, as the generation technologies on the market during base hours are cleaner than during peak hours (when greater demand must be met, and this is done with dirtier technologies). Therefore, if BESS systems are charged with cheaper and cleaner energy, the companies that use them will reduce their costs and CO2 emissions.
Read also: Peak Shaving: transforming energy savings
In summary, implementing these tools, together with efficient energy management, can generate significant savings on CFE bills and improve the competitiveness of industrial companies. At Industronic, we have the tools and equipment necessary to support you in your business strategies for electrical energy efficiency. In addition, we can create customized and hybrid projects that combine different solutions and generate greater benefits.

At Industronic, we have a specialized team to advise you.
Consult our specialists and get advice on optimizing your electricity consumption and efficiency.