An introduction to UPS batteries
Let us first define what a battery is. It is an electrical device consisting of one or more electrochemical cells that can convert stored chemical energy into direct current voltage (DCV). UPS batteries are the main element, since they are the ones that provide backup power to the UPS system.
The characteristics that define a battery are:
- Amount of energy, is the amount of energy it can store (Wh).
- Maximum current, it is the current it can deliver when discharged (A).
- Depth of discharge, represents the amount of energy that is extracted and can sustain the battery in the discharge (%).
What type of batteries does a UPS use?
Batteries have a charge capacity according to their composition, which is measured in ampere-hours (Ah), that is, the amount of amperes of current throughout a continuous hour of life. The higher its charge capacity, the more current it can store inside.
The most commonly used batteries in UPS are:
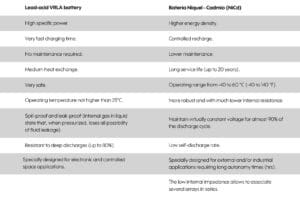
- Lead-acid batteries with VRLA technology.
- Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries.

Lead-Acid Battery
However, the batteries in their electronic use (UPS), are manufactured with VRLA (valve regulated lead acid) technology, commonly known as sealed battery or maintenance free battery. The advantage is that they do not require forced ventilation, can be installed in small spaces, can be mounted in any orientation (except downwards) and do not require constant maintenance.
This type of batteries in particular are manufactured in 2V, 6V and 12V. Being lead-acid, they are very heavy and therefore their energy capacity is directly proportional to their size-weight.
In applications that require optimized performance, AGM (Absorption Glass Mat) and Gel (The electrolyte used has a jelly-like appearance) technologies are used in their manufacture; these technologies are deep discharge.
Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd) Battery
On the other hand, the structural component of the plate is steel, the plates do not gradually weaken through repeated cycling, giving them an exceptionally long service life.
This battery technology is used in applications requiring extended backup (hrs) operation and more hostile temperature and humidity conditions.
They can be overcharged, can continue to be charged when no more charge is available, and can withstand a wide range of operating temperatures. The Nickel-Cadmium battery is normally for industrial use.

How are UPS batteries recharged?
UPS have a Smart Charger, which optimizes faster recharging and helps prolong battery life.
These chargers check the state of the battery during the charging process, supply as much current as necessary and when the battery is full, reduce the current flow (or supply current pulses at intervals) to keep the battery in its maximum state without damaging it.
During this recharge cycle, a test run is performed to validate proper battery charging and/or to report battery performance problems.
Both types of batteries should usually be charged in stages (Smart Charger), the first recharge cycle is the fastest as the battery reaches again between 70% – 80% of its capacity in a short period of time and the following stages are designed to reach 100% of its recharge keeping the battery in optimal conditions (without stressing the battery).
Both Nickel-Cadmium and Lead-Acid VRLA batteries can be severely damaged if discharged below 75% of their rated voltage. With either system, you should never let the battery run down completely (UPSs limit the minimum operating voltage of the batteries).
Advantages of UPS batteries
Explore our UPS battery catalog and contact us if you need advice. Our customer service and technical support team is trained to answer your questions and provide you with the necessary guidance.