Voltage (V) in terms of electricity is also known as electrical voltage. In fact, the correct term is electrical voltage when talking about alternating current voltage. This voltage is the one we have in the home, in the company, in the factory or any place where we work with equipment connected to an outlet.
What is the voltage in Mexico?
In Mexico, the standard light voltage for most homes and businesses is 127 volts (V) at a frequency of 60 Hertz (Hz). However, it is important to note that there are two types of voltage in the country:
Single-phase: 120 volts phase-neutral and 240 volts phase-phase.
Three-phase: 127 volts phase-neutral and 220 volts phase-phase.
Three-phase arrangements are also available in:
Three-phase: 110 volt phase-neutral and 190 volt phase-phase
Three-phase: 115 volts phase-neutral and 220 volts phase-phase
Three-phase: 120 volt phase-neutral and 208 volt phase-phase
In the industrial sector it is usual to use operating voltages of:
Three-phase: 254 volts phase-to-neutral and 440 volts phase-to-phase.
Three-phase: 266 volts phase-neutral and 460 volts phase-phase
Three-phase: 277 volts phase-neutral and 480 volts phase-phase
Voltage types in Mexico
According to Hector Mondragon, Monterrey Sales Manager, “There are two types of voltage in Mexico: direct current voltage and alternating current voltage. The Federal Electricity Commission (CFE) in Mexico supplies the alternating current voltage”.
Let’s remember that, for electricity to flow, it is necessary the electric tension or better known as voltage (V). This is classified into low, medium and high voltage levels.
- Low voltage: it comprises a range that goes from 100 V to 1000 V. Its main function is to supply electric power to homes, industry and public lighting, although voltage levels vary slightly. In the case of public lighting and households, voltages of 110 V and 220 V are used, respectively, while in industry, voltages of 220 V and 440 V can be used.
- Medium voltage: refers to levels higher than 1000 V and reaching up to 34.5 kV. It is generally used to distribute electricity from substations to transformer banks. In Mexico, these facilities operate with a voltage ranging from 1 kV to 25 kV.
- High voltage: it ranges from 34.5 kV to 230 kV. This type of voltage is mainly used to transport electricity over long distances, reaching substations where it is transformed into medium voltage. Due to their high voltage level, these installations require thick cables and high insulators for their proper operation.
Differences between voltage, power and current
These three concepts are closely related and are necessary to know how electricity works. Understanding their differences is important in order not to confuse them as synonyms.
Voltage:
Voltage allows the transfer of energy from a negative to a positive point. It is measured in volts (V) and determines the strength with which electric current flows. For example, when plugging a device into an electrical outlet, there are usually two holes. One in charge of the positive charge and one in charge of the negative charge; between the two there is a voltage difference which is what makes it possible to get to generate electrical power.
Power:
In simple terms, electrical power is defined as the amount of energy that a device consumes or generates in a specific interval of time. It is expressed in watts (W) and is calculated by multiplying the voltage by the current. This measurement allows us to understand how much energy is being used or produced by an electrical device at any given time.
Current:
Current intensity is the magnitude that determines the rate at which a certain amount of electrical charge will flow through a circuit. Current is measured in amperes (A) and its value is obtained by dividing the voltage by the resistance of the circuit.
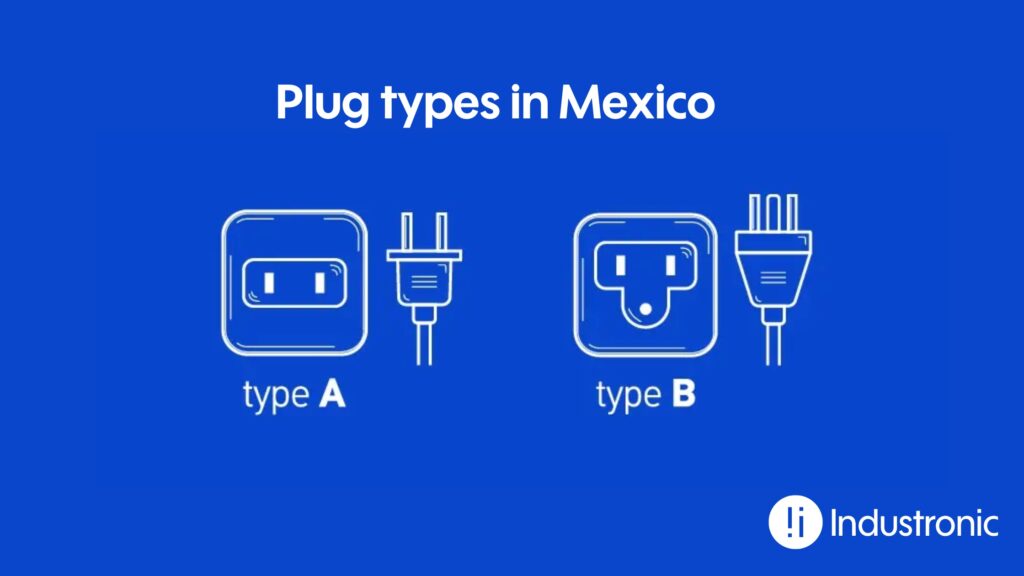
Types of plugs and sockets in Mexico
In Mexico, plugs and sockets are type A and B.
- Type A plug: two flat pins, also used in the United States and Canada.
- Type B plug: It has two flat pins and a round ground pin, also used in Japan.
Why must the voltage and frequency match?
If a device is connected to a different voltage or frequency than specified, it runs the risk of damage or even fire. Generally, electrical devices are designed to operate with domestic voltage in Mexico of 110 V or 220 V and frequencies of 50 or 60 Hz. If any of these values do not match, the use of a power converter will be required.
According to information from the Mexican Ministry of Foreign Affairs, devices marked “110-220V frequency 50-60Hz” are designed to adapt to different electrical environments and are suitable for use in any location. This usually applies to digital camera chargers, laptop computers and cellular phones, which are prepared to operate at various voltages. However, it is essential to verify this compatibility to avoid mishaps.
In conclusion, it is essential to understand from the standard voltage differences in Mexican homes, to the different voltages present in industry and public infrastructure, to avoid irreparable damage to devices and to ensure a safe and efficient electrical environment.
At Industronic, we understand the importance of maintaining precise control over the electrical supply, which is why we offer a wide range of products designed to meet the specific needs of each customer.
